
Who does not want their webpage to appear on the first page of Google or other search results? To rank on the 1st page of Google, your website needs to pass a few acid tests!
Before we tell you what the key acid tests are, small business owners and entrepreneurs, need to understand a few things that google or a search engine does when it recognizes your website for the first time.
1. Crawling :
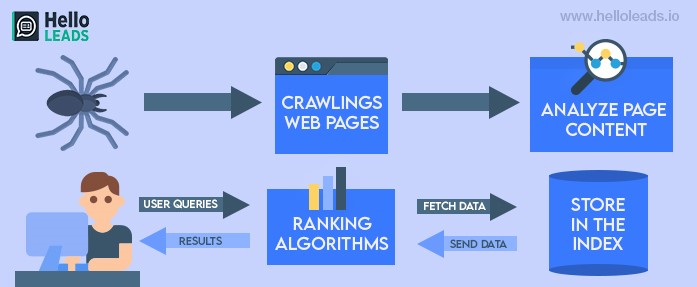
Google usually crawls and discovers new websites and web pages on its own.
Some pages are known to Google because it has already visited them once before. Other pages are discovered when Google follows a link from a known page to a new page. It is also possible to submit a sitemap so that Google knows what to crawl.
2. Indexing :
Indexing is the process by which google understands your webpage fully. Once indexed the information is stored in an index file by google and used later for searching. One way to help google index your page properly is to have proper and meaningful titles. Make sure every page on your site has a title specified in the <title> element.
3. Ranking and Serving :
Once indexed, for any search (involving a keyword or a set of keywords) google finds the best-matched results and serves you as search results.
Now, welcome to the acid test!
Now, if you are a small business owner or a website developer meeting the needs of businesses, you would be interested in getting the website on the first page of google search results. To achieve this, you need to make sure certain parameters are in place.
Web Vitals is an initiative by Google to determine how good is your website. This part of a measure called Page experience measures how users perceive the experience of interacting with a web page beyond its content and information.
Web Vitals consist of 3 main elements each focusing on (1) loading, (2) interactivity, and (3) visual stability. Added to this (4) mobile friendliness and (5) secure connection. Together if you pass these 5 tests, your website would rank much higher.
Let us see what each one of them means in detail :
Core Web Vitals:
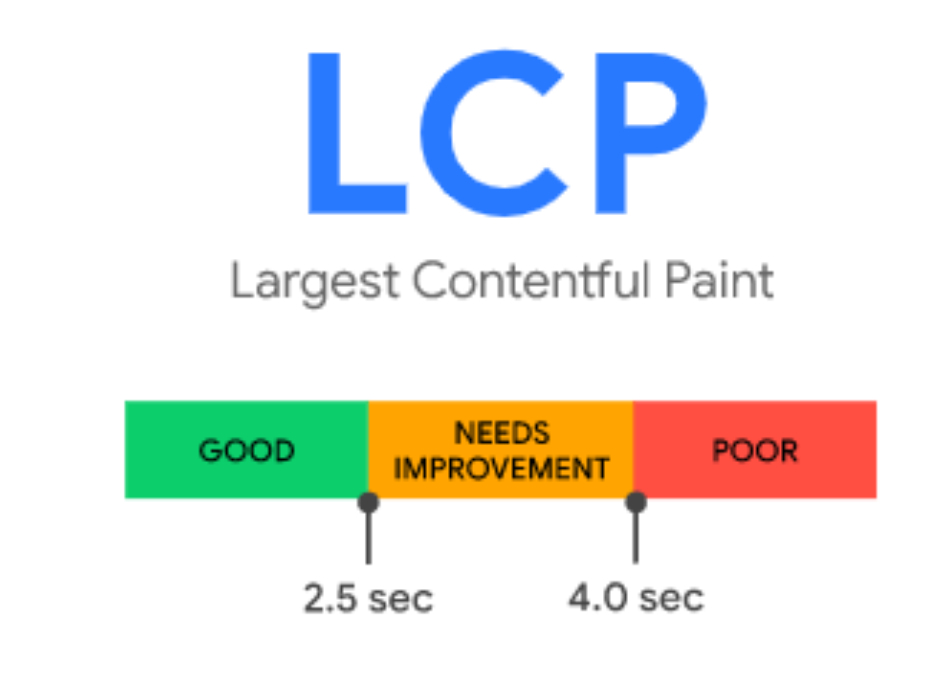
(1) Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) : measures loading performance. To provide a good user experience, LCP should occur within 2.5 seconds of when the page first starts loading.
(2) First Input Delay (FID) : measures interactivity. To provide a good user experience, pages should have an FID of 100 milliseconds or less.

(3) Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) : measures visual stability. To provide a good user experience, pages should maintain a CLS of 0.1. or less.
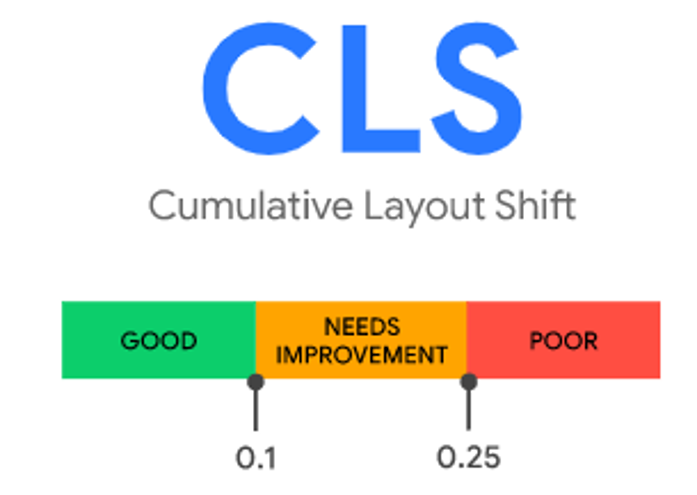
Avoid all unexpected layout shifts by following these few guiding principles:
- Always include size attributes on your images and video elements, or otherwise reserve the required space with something like CSS aspect ratio boxes.
- Never insert content above existing content, except in response to user interaction.
- Prefer to transform animations to animations of properties that trigger layout changes.


As per Google Search Central “ The page experience ranking signal went into effect for mobile devices in August 2021. We’ll begin using page experience as part of our desktop ranking systems beginning in February 2022. The rollout will be complete by the end of March 2022. This ranking launch will be based on the same page experience signals that we rolled out for mobile in August 2021.”
“ While page experience is important, Google still seeks to rank pages with the best information overall, even if the page experience is subpar. Great page experience doesn’t override having great page content. However, in cases where many pages may be similar in relevance, page experience can be much more important for visibility in Search.” said Google Search Central.
(4) Is your web page mobile-friendly?
Mobile-friendliness refers to how well a website can be accessed from a mobile device, such as a phone or tablet. In light of the rise of mobile internet usage, Google has shifted to a “mobile-first index”. Google’s crawlers will read your mobile site first as a result. If your website is not mobile-friendly, you will perform poorly in search engine results, which will lead to decreased traffic, fewer leads, and less revenue.
Is your website Mobile-Friendly?
Mobile-friendliness is therefore vital for SEO if your website targets more traffic. In Google and Bing’s algorithms, it’s a ranking signal that signals a user is using a mobile device to search. A mobile-friendly website, in general, will be ranked higher on mobile search results than a non-mobile-friendly site.
To check if your website is a mobile-friendly website, follow any of the below-listed ways.
- Enter your website URL on the Mobile-Friendly Test page and check the results.
- Enter your website URL on Google’s PageSpeed insights and click Analyze to check the performance of your website on mobile
- Check the mobile usability of your website property on the respective Google Search console page. Pages without issues will be shown as Valid and Pages with issues will be shown as Error.
It’s simple to make your website mobile-friendly if it’s based on content consumption, such as if your business relies on consumers coming to your site to read articles or watch videos. Use Google’s Accelerated Mobile Pages Project (AMP). AMP is an open-source standard that enables you to create websites that load extremely fast on mobile devices. AMP works as below:
- A limited set of custom HTML properties, used by AMP, is used to determine the aspect ratio of assets so browsers know what the page will look like before it is rendered.
- ATF(above the fold) content is prioritized over other requests in the page’s entire load chain with AMP JavaScript. As a result, visitors can start reading/watching almost immediately after arriving
- With the predetermined layout and asynchronous loading, visitors won’t encounter choppy and jumping page rendering.
(5) Check if a site’s connection is secure
To see whether your website is safe to visit, you can check for security info about the site. Chrome will alert you if you can’t visit the site safely or privately.
- In Chrome, open a page.
- To check a site’s security, to the left of the web address, look at the security status:

- Secure
- Info or not secure
- Not secure or Dangerous
3. To see the site’s details and permissions, select the icon. You’ll see a summary of how private Chrome thinks the connection is.
If your site is not secure, Google search central suggests you adopt HTTPS than HTTP to protect your user’s connection to your website. It is SSL certificates that enable websites to move from HTTP to HTTPS. Having an SSL certificate ensures that user information is secure, verifies ownership of a website, prevents attackers from creating a fake version, and gains user trust.
SSL certificates are valid only when issued by a Certificate Authority (CA). CA is an outside organization, a trusted third party, which generates and distributes SSL certificates. Additionally, the Certificate Authority will digitally sign the certificate with its private key, allowing clients to verify it. As soon as the certificate is issued, it needs to be installed and activated on the website’s origin server. The website can load over HTTPS once it has been activated on the origin server, and all traffic to and from the website is encrypted and secure.
Tools that can help you
Chrome User Experience Report
PageSpeed Insights
Search Console (Core Web Vitals report)
web-vitals JavaScript library
Chrome DevTools
Lighthouse
WebPageTest
Mobile-Friendly tests
Keep coming back to HelloLeads insights and blogs to learn more about improving your business visibility digitally.
Share this blog :










